Primary Secondary Failover of StoneDB
StoneDB can be deployed in a primary/secondary solution to implement manual or automatic failover. Implementing automatic failover often requires the assist of third-party middleware. After automatic failover is enabled, services will be automatically switched to the secondary node if the primary node fails. The example provided in this topic uses third-party middleware Replication Manager to describe how to implement automatic failover.
The following table provides the environment configurations:
| IP Address | Memory | CPU | OS | Role | Database/Middleware |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 192.168.30.40 | 8 GB | 8 cores | CentOS Linux release 7.9 | Primary | MySQL 5.7 |
| 192.168.30.41 | 8 GB | 8 cores | CentOS Linux release 7.9 | N/A | Replication Manager 2.2 |
| 192.168.30.42 | 8 GB | 8 cores | CentOS Linux release 7.9 | Secondary | MySQL 5.7 |
| 192.168.30.46 | 16 GB | 16 cores | CentOS Linux release 7.9 | Secondary | StoneDB 5.7 |
- The configurations of the four servers are consistent, except that the server on which StoneDB is deployed provides larger memory and more CPU cores. This is because StoneDB needs to replay binlogs and process analytical queries. These operations are resource consuming.
- We recommend that the databases deployed on primary and secondary nodes are consistent in version.
The architecture contains one primary node and two secondary nodes, because the secondary node on which Tianmu is deployed will not participate in primary/secondary failover.
- In the primary node (192.168.30.40), the InnoDB engine is used to process read and write operations in transactions. The primary node is a read-write node.
- In secondary node 1 (192.168.30.42), the InnoDB engine is used to synchronize data from the primary node. The secondary node is a read-only node. If the primary node fails, services will be automatically switched to secondary node 1 to ensure smooth service running.
- In secondary node 2 (192.168.30.46), the Tianmu engine is used only to process read operations required by analytical queries.
Step 1. Check the system environment
Perform the following sub-steps on each of the four nodes:
1.1 Disable the firewall
# systemctl stop firewalld
# systemctl disable firewalld
1.2 Disable SELinux
# vim /etc/selinux/config
SELINUX = disabled
1.3 Disable swap
Change the value of vm.swappiness to 1 to disable swap.
# vi /etc/sysctl.conf
vm.swappiness = 1
1.4 Modify the limits of the OS
# ulimit -a
core file size (blocks, -c) 0
data seg size (kbytes, -d) unlimited
scheduling priority (-e) 0
file size (blocks, -f) unlimited
pending signals (-i) 1031433
max locked memory (kbytes, -l) 64
max memory size (kbytes, -m) unlimited
open files (-n) 65535
pipe size (512 bytes, -p) 8
POSIX message queues (bytes, -q) 819200
real-time priority (-r) 0
stack size (kbytes, -s) 10240
cpu time (seconds, -t) unlimited
max user processes (-u) 1024
virtual memory (kbytes, -v) unlimited
file locks (-x) unlimited
# Modify the soft and hard limits of the OS.
# vim /etc/security/limits.conf
* soft nofile 65535
* hard nofile 65535
mysql soft nproc 1028056
mysql hard nproc 1028056
1.5 Create a user
# groupadd mysql
# useradd -g mysql mysql
# passwd mysql
This sub-step is not required for the node on which Replication Manager is deployed.
After all the sub-steps are complete on a node, restart the OS of the node.
Step 2. Deploy MySQL
On each of server 192.168.30.40 and server 192.168.30.42, perform the following sub-steps to deploy MySQL.
2.1 Download the installation package
Download the installation package of MySQL 5.7.
2.2 Uninstall MariaDB
# rpm -qa|grep mariadb
mariadb-5.5.56-2.el7.x86_64
mariadb-server-5.5.56-2.el7.x86_64
mariadb-libs-5.5.56-2.el7.x86_64
# yum remove mariadb*
# rpm -qa|grep mariadb
2.3 Upload and decompress the TAR package
# tar -zxvf mysql-5.7.36-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.gz -C /usr/local/
# cd /usr/local/
# mv mysql-5.7.36-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64 mysql
2.4 Create directories
# mkdir -p /mysql/data/
# mkdir -p /mysql/log
# chown -R mysql:mysql /mysql/
2.5 Configure parameter file my.cnf
On the primary node:
# vim /etc/my.cnf
[client]
port = 3306
socket = /mysql/data/mysql.sock
[mysqld]
port = 3306
basedir = /usr/local/mysql
datadir = /mysql/data
socket = /mysql/data/mysql.sock
pid_file = /mysql/data/mysqld.pid
log_error = /mysql/log/mysqld.log
log_bin = /mysql/log/mybinlog
server_id = 40
character_set_server = utf8mb4
collation_server = utf8mb4_general_ci
max_connections = 1000
binlog_format = row
default_storage_engine = innodb
read_only=0
innodb_buffer_pool_size = 4096000000
innodb_log_file_size = 1024000000
innodb_log_files_in_group = 3
innodb_io_capacity = 4000
innodb_io_capacity_max = 8000
# Enabe the GTID mode.
gtid_mode = on
enforce_gtid_consistency = 1
# Parallel replication
binlog_transaction_dependency_tracking = WRITESET
transaction_write_set_extraction = XXHASH64
On the secondary node 1:
# vim /etc/my.cnf
[client]
port = 3306
socket = /mysql/data/mysql.sock
[mysqld]
port = 3306
basedir = /usr/local/mysql
datadir = /mysql/data
socket = /mysql/data/mysql.sock
pid_file = /mysql/data/mysqld.pid
log_error = /mysql/log/mysqld.log
log_bin = /mysql/log/mybinlog
server_id = 42
character_set_server = utf8mb4
collation_server = utf8mb4_general_ci
max_connections = 1000
binlog_format = row
default_storage_engine = innodb
read_only=1
innodb_buffer_pool_size = 4096000000
innodb_log_file_size = 1024000000
innodb_log_files_in_group = 3
innodb_io_capacity = 4000
innodb_io_capacity_max = 8000
# Enabe the GTID mode.
gtid_mode = on
enforce_gtid_consistency = 1
# Parallel replication
binlog_transaction_dependency_tracking = WRITESET
transaction_write_set_extraction 6= 4
2.6 Initialize the instance
/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqld --defaults-file=/etc/my.cnf --initialize --user=mysql
2.7 Start the instance
/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqld_safe --defaults-file=/etc/my.cnf --user=mysql &
The temporary password of the administrator account is saved in mysqld.log. After the initial login, you must change the password.
Step 3. Deploy StoneDB
3.1 Download the installation package
Download the installation package of StoneDB_5.7.
3.2 Upload and decompress the TAR package
# cd /
# tar -zxvf stonedb-ce-5.7-v1.0.0.el7.x86_64.tar.gz
You can upload the installation package to the server (192.168.30.46) based on the installation instructions. The directory extracted from the installation package is stonedb57. In this example, the installation path is /stonedb57.
3.3 Check the dependencies
# cd /stonedb57/install/bin
# ldd mysqld
# ldd mysql
If the command output contains keywords not found, some dependencies are missing and must be installed. For example, libsnappy.so.1 => not found is returned.
- If your OS is Ubuntu, run the
sudo apt search libsnappycommand. The command output will inform you to install libsnappy-dev. - If your OS is RHEL or CentOS, run the
yum search all snappycommand. The command output will inform you to install snappy-devel and snappy.
3.4 Create directories
mkdir -p /stonedb57/install/data
mkdir -p /stonedb57/install/binlog
mkdir -p /stonedb57/install/log
mkdir -p /stonedb57/install/tmp
mkdir -p /stonedb57/install/redolog
mkdir -p /stonedb57/install/undolog
chown -R mysql:mysql /stonedb57
3.5 Configure parameter file my.cnf
# vim /stonedb57/install/my.cnf
[client]
port = 3306
socket = /stonedb57/install/tmp/mysql.sock
[mysqld]
port = 3306
basedir = /stonedb57/install/
datadir = /stonedb57/install/data
socket = /stonedb57/install/tmp/mysql.sock
pid_file = /stonedb57/install/data/mysqld.pid
log_error = /stonedb57/install/log/mysqld.log
log_bin = /stonedb57/install/binlog/binlog
server_id = 46
character_set_server = utf8mb4
collation_server = utf8mb4_general_ci
max_connections = 1000
binlog_format = row
default_storage_engine = tianmu
read_only=1
innodb_buffer_pool_size = 2048000000
innodb_log_file_size = 1024000000
innodb_log_files_in_group = 3
innodb_io_capacity = 4000
innodb_io_capacity_max = 8000
innodb_log_group_home_dir = /stonedb57/install/redolog/
innodb_undo_directory = /stonedb57/install/undolog/
innodb_undo_log_truncate = 1
innodb_undo_tablespaces = 3
innodb_undo_logs = 128
# Enable the GTID mode
gtid_mode = on
enforce_gtid_consistency = 1
# Parallel replication
slave_parallel_type = LOGICAL_CLOCK
slave_parallel_workers = 8
3.6 Initialize the instance
/stonedb57/install/bin/mysqld --defaults-file=/stonedb57/install/my.cnf --initialize --user=mysql
3.7 Start the instance
/stonedb57/install/bin/mysqld_safe --defaults-file=/stonedb57/install/my.cnf --user=mysql &
The temporary password of the administrator account is saved in mysqld.log. After the initial login, you must change the password.
Step 4. Configure primary/secondary replication
4.1 Create a replication user
create user 'repl'@'%' identified by 'mysql123';
grant replication slave on *.* to 'repl'@'%';
4.2 Back up the primary database
/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqldump -uroot -pmysql123 --single-transaction --set-gtid-purged=on -B aa > /tmp/aa.sql
4.3 Transfer the backup file
scp /tmp/aa.sql root@192.168.30.42:/tmp
scp /tmp/aa.sql root@192.168.30.43:/tmp
If the backup file is too large, we recommend that you use MyDumper to transfer the file.
4.4 Recover secondary node 1
/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysql -uroot -pmysql123 -S /mysqldb/data/mysql.sock
source /tmp/aa.sql
Before performing this operation, ensure that gtid_executed is empty.
4.5 Recover secondary node 2
Before recovering secondary node 2, change the storage engine from InnoDB to Tianmu and comment out the UNLOCK TABLES and LOCK TABLES statements.
sed -i 's/UNLOCK TABLES/-- UNLOCK TABLES/g' /tmp/aa.sql
sed -i 's/LOCK TABLES `/-- LOCK TABLES `/g' /tmp/aa.sql
sed -i 's/ENGINE=InnoDB/ENGINE=tianmu/g' /tmp/aa.sql
/stonedb57/install/bin/mysql -uroot -pmysql123 -S /stonedb57/install/tmp/mysql.sock
source /tmp/aa.sql
Before performing this operation, ensure that gtid_executed is empty.
4.6 Configure primary/secondary replication
On secondary node 1:
CHANGE MASTER TO
MASTER_HOST='192.168.30.40',
MASTER_PORT=3306,
MASTER_USER='repl',
MASTER_PASSWORD='mysql123',
MASTER_AUTO_POSITION = 1;
start slave;
show slave status\G
On secondary node 2:
CHANGE MASTER TO
MASTER_HOST='192.168.30.40',
MASTER_PORT=3306,
MASTER_USER='repl',
MASTER_PASSWORD='mysql123',
MASTER_AUTO_POSITION = 1;
start slave;
show slave status\G
Step 5. Configure Replication Manager
5.1 Configure file hosts
Configure file hosts on each node.
# vim /etc/hosts
192.168.30.40 HAMI01
192.168.30.41 HAMI02
192.168.30.42 HAMI03
192.168.30.46 HAST05
5.2 Configure passwordless login
On the node on which Replication Manager is deployed, configure the following items:
ssh-keygen
ssh-copy-id HAMI01
ssh-copy-id HAMI03
ssh-copy-id HAST05
ssh HAMI01
ssh HAMI03
ssh HAST05
5.3 Configure YUM sources
# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/signal18.repo
[signal18]
name=Signal18 repositories
baseurl=http://repo.signal18.io/centos/2.1/$releasever/$basearch/
gpgcheck=0
enabled=1
5.4 Install Replication Manager
# yum install -y replication-manager-osc
# rpm -qa|grep replication
replication-manager-osc-2.2.20-1.x86_64
5.5 Create a monitoring account for the primary database
create user 'rep_monitor'@'%' identified by 'mysql123';
grant reload, process, super, replication slave, replication client, event ON *.* to 'rep_monitor'@'%';
grant select ON mysql.event to 'rep_monitor'@'%';
grant select ON mysql.user to 'rep_monitor'@'%';
grant select ON performance_schema.* to 'rep_monitor'@'%';
5.6 Configure config.toml
# vim /etc/replication-manager/config.toml
# Cluster name
[StoneDB-HA]
# Primary/Secondary node
db-servers-hosts = "192.168.30.40:3306,192.168.30.42:3306,192.168.30.46:3306"
# Primary node
db-servers-prefered-master = "192.168.30.40:3306"
# Monitoring account
db-servers-credential = "rep_monitor:mysql123"
db-servers-connect-timeout = 2
# Replication account
replication-credential = "repl:mysql123"
# The node on which Tianmu is deployed does not partiticate in failover.
db-servers-ignored-hosts="192.168.30.46:3306"
##############
## FAILOVER ##
##############
# Automatic failover
failover-mode = "automatic"
# If another failure occurs within 30s after a failover, the system will not trigger another failover in case that the failure is caused by a hardware fault or network problem.
failover-time-limit=30
[Default]
#########
## LOG ##
#########
log-file = "/var/log/replication-manager.log"
log-heartbeat = false
log-syslog = false
monitoring-datadir = "/var/lib/replication-manager"
log-level=1
replication-multi-master = false
replication-multi-tier-slave = false
failover-readonly-state = true
http-server = true
http-bind-address = "0.0.0.0"
http-port = "10001"
5.7 Start Replication Manager
# systemctl start replication-manager
# netstat -lntp|grep replication
tcp6 0 0 :::10001 :::* LISTEN 13128/replication-m
tcp6 0 0 :::10005 :::* LISTEN 13128/replication-m
5.8 Log in to Replication Manager
Login address: http://192.168.30.41:10001
The default username and password are admin and repman.
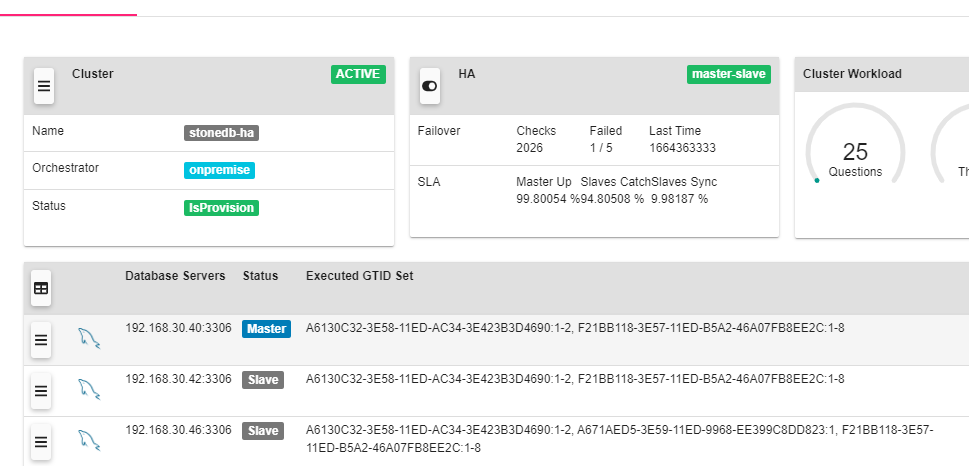
More information
- We recommend that you enable the GTID mode.
- We recommend that you set the primary/secondary replication mode to semi-sync replication.
- The node on which the Tianmu engine is deployed does not participate in the primary/secondary failover.